La L-leucina es uno de los nueve aminoácidos esenciales, lo que significa que el organismo no puede producirlo por sí mismo y debe obtenerse a través de la dieta.


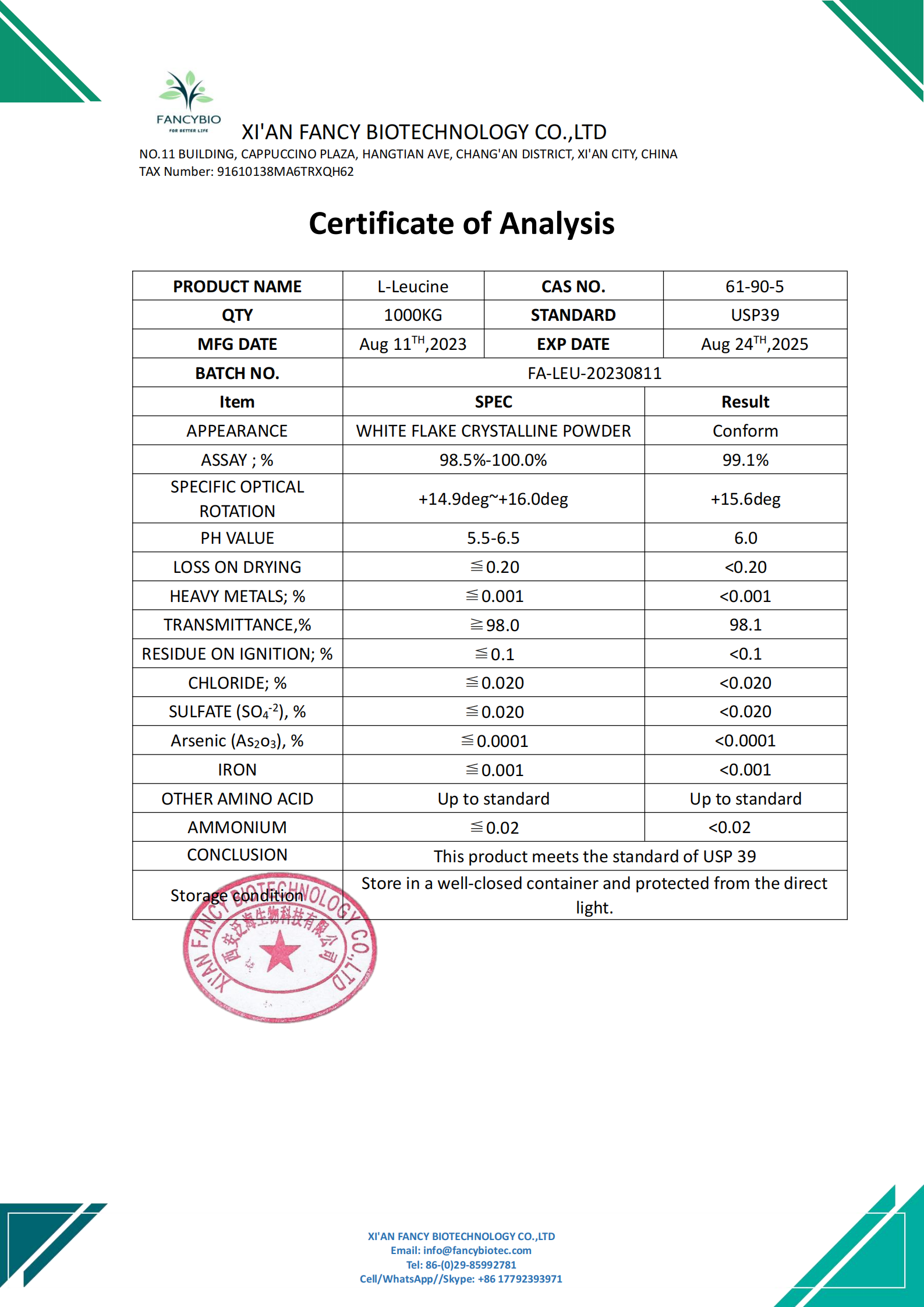
L-Leucina CAS NO. 61-90-5
La L-leucina es uno de los nueve aminoácidos esenciales, lo que significa que el organismo no puede producirlo por sí mismo y debe obtenerse a través de la dieta.
La L-Leucina es un polvo o gránulo cristalino de color blanco. Es uno de los aminoácidos esenciales para el cuerpo humano. No puede sintetizarse por sí mismo y debe ingerirse a través de la dieta. Como parte de los aminoácidos de cadena ramificada (BCAA), desempeña un papel clave en la síntesis de proteínas y la reparación muscular, especialmente ayudando a promover el crecimiento muscular y la recuperación después del ejercicio. La L-leucina también puede ayudar a regular los niveles de azúcar en sangre, mejorar el metabolismo energético y ralentizar la degradación muscular, lo que resulta especialmente beneficioso para atletas y entusiastas del fitness. Además, la leucina también tiene ciertos efectos en la mejora de la inmunidad en el cuerpo y el apoyo a la función hepática, y se utiliza a menudo como un suplemento dietético.
Funciones y aplicaciones:
1 Síntesis proteica: La L-Leucina es un regulador clave de la síntesis de proteínas, especialmente en el tejido muscular. Activa una vía conocida como la vía de la diana de rapamicina en mamíferos (mTOR), que estimula la síntesis de proteínas musculares. Esto hace que la leucina sea especialmente importante para los atletas, culturistas y personas que buscan optimizar el crecimiento muscular y la recuperación.
2 Crecimiento y reparación muscular: L-Leucina se utiliza comúnmente en suplementos de nutrición deportiva, a menudo en combinación con otros aminoácidos de cadena ramificada (BCAA), para apoyar el crecimiento muscular y la reparación. Ayuda a mantener la masa muscular durante periodos de ejercicio, dietas o lesiones, promoviendo la síntesis de proteínas e inhibiendo su degradación.
3 Producción de energía: Más allá de su papel en la síntesis de proteínas, la L-leucina también puede oxidarse dentro de las células musculares para proporcionar energía durante el ejercicio prolongado o períodos de ayuno. Sirve como sustrato para la producción de acetil-CoA, una molécula clave en las vías de producción de energía del cuerpo.
4 Regulación de los niveles de azúcar en sangre: Se ha demostrado que la L-Leucina desempeña un papel en la regulación de los niveles de azúcar en sangre y la secreción de insulina. Puede aumentar la sensibilidad a la insulina, ayudando a mejorar la captación de glucosa por las células musculares y reducir el riesgo de resistencia a la insulina y diabetes tipo 2.
5 Regulación del apetito: Algunas investigaciones sugieren que la L-leucina puede desempeñar un papel en la regulación del apetito y la saciedad. Puede ayudar a reducir la ingesta de alimentos mediante la promoción de la liberación de hormonas que señalan la saciedad, ayudando potencialmente en los esfuerzos de control de peso.
6 Cicatrización de heridas: La L-leucina participa en la síntesis de colágeno y otras proteínas estructurales necesarias para la cicatrización de heridas y la reparación de tejidos. Contribuye a la formación de nuevo tejido y al restablecimiento de la integridad de la piel tras una lesión o intervención quirúrgica.
7 Fuentes dietéticas: Entre los alimentos ricos en L-leucina se encuentran la carne (sobre todo de ternera, pollo y cerdo), el pescado, los productos lácteos (como el queso, la leche y el yogur), los huevos, las legumbres (como las alubias y las lentejas), los frutos secos, las semillas y ciertos cereales (como el trigo y el arroz).
Our professional sales team are waiting for your consultation.